
Stacked bar graphs require specific labelling, but they can be very helpful if you want to understand different segments within the same category. Different colours can help to distinguish between the subcategories within a data set. A stacked bar graph can display data either horizontally or vertically. This graph, also known as the composite bar graph, helps you to compare variables by dividing categories of information into subcategories and stacking them in a single rectangular bar.
#Sales and expense bar graph how to
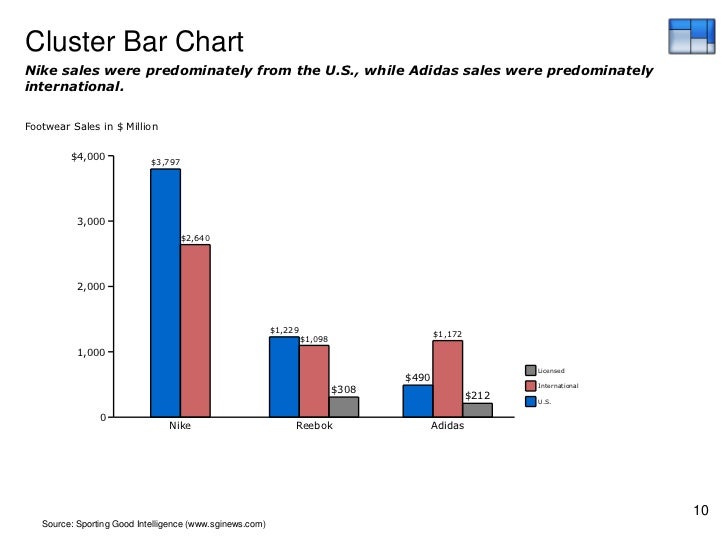
Related: How to Learn Data Entry and Available Career Options Stacked bar graph Grouped bar graphs can present data vertically or horizontally. Sometimes known as clustered bar graphs, grouped bar graphs can appear more complex as the amount of information presented increases, so using colours to distinguish between subcategories can be useful. For example, you may want to look at your monthly expenses by expense categories, such as food, rent, transport, and entertainment. In addition to comparing categories, this type of graph can show the subcategories of each variable or data set.

Horizontal bar graphs work when you want to compare data between theoretical variables because there's more space for textual information on the x-axis. The horizontal bar graph represents data horizontally using rectangular bars on the y-axis while the length of each bar corresponds with a value on the x-axis. This graph is the same as the vertical bar graph except that the bars are horizontal rather than vertical. In this type of graph, you arrange the bars vertically on the x-axis, and the height of each bar corresponds with a value on the y-axis. Sometimes known as a column graph, this graph represents data vertically using rectangular bars on a chart. The most commonly used bar graph is the vertical bar graph. The following are some key features of each type of bar graph that highlight their differences: Vertical bar graph Beyond these two types, there's the grouped bar graph and the stacked bar graph, both of which can present data vertically or horizontally. There are a few types of bar graphs with two main classifications: the vertical bar graph and the horizontal bar graph. Related: How to Become a Big Data Analyst (With Salary Expectations) Types of bar graphs They can also help to predict future events based on previous data trends. Researchers typically use these graphs to showcase important information about a particular variable. The horizontal and vertical lines, also known as the x-axis and the y-axis respectively, usually have labels, such as category titles, numbers, and scale ranges.Ī bar graph is a valuable tool for organizing and providing a visual display of numerical values. They display the collected data with rectangular bars, placed either vertically or horizontally, on a chart. Bar graphs, also known as bar charts, present categorical information. What is a bar graph?Ī bar graph is a visual representation of quantifiable or statistical data sets.
In this article, we review the different types of bar graphs, outline their advantages and disadvantages, provide a step-by-step guide to creating a bar graph, and compare them to histograms. Understanding different bar graphs can broaden your knowledge of data sets and enhance your ability to present visual statistics. Determining the most suitable type of bar graph to use depends on the data you want to compare and how you want to present them. There are several types of bar graphs, each with a specific purpose, that can help you to present categorical information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
